How many types of cervical spondylosis? With today’s lifestyle changes, the prevalence of cervical spondylosis has also increased. This disease is related to factors such as the cervical spine’s long-term strain, bone hyperplasia, thickening of ligaments, or prolapse of the intervertebral disc.



Under the influence of these factors, nerve roots, vertebral arteries, cervical spinal cord, and other parts will be compressed. Then the sympathetic nerves will be stimulated, resulting in a series of dysfunctional symptoms.
The disease can be divided into several types depending on the tissues and structures involved. So what types are there?
1. Nerve root type
The nerve root type has the highest incidence of the disease, accounting for about 60% to 70%. The main lesions of this type are narrowing of the interlunar foramen and compression of the cervical nerve roots.
The most common age group for this type is 30 to 50 years old. The patient will have neck pain and stiffness in the early stage, and radiating pain or numbness in the upper limbs.
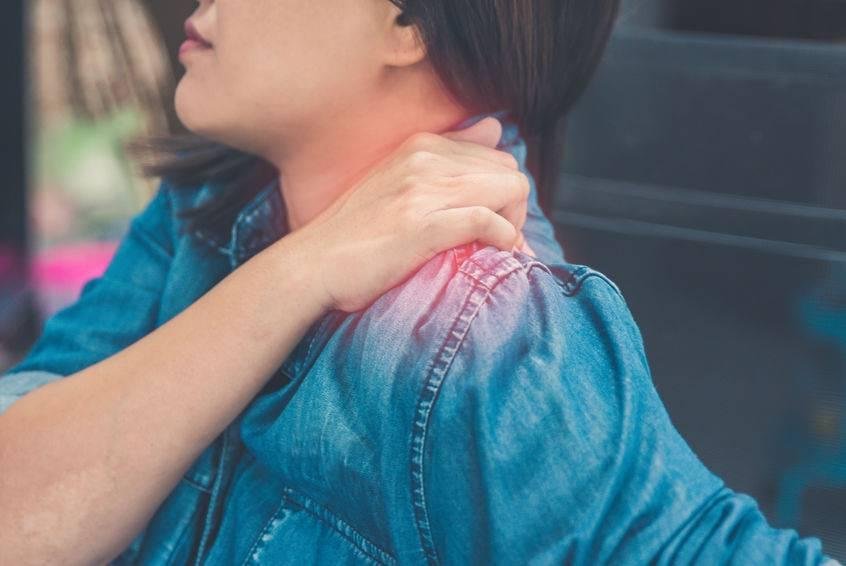



Pain and numbness radiate along the direction of the compressed nerve root. When the head or bad posture suddenly involves the affected limb, the patient will experience severe sharp pain.
In severe cases, patients will have symptoms of heaviness and weakness in the upper limbs, and sometimes objects in their hands will fall.
In addition, patients may also have vasomotor symptoms, such as no sweating, swelling, or pain in the hands. In advanced stages, there may also be muscle atrophy and chest pain.
Chest pain is mainly manifested as the slow-onset intractable unilateral pectoralis major and posterior breast pain, which is related to bone spur compression and intervertebral disc herniation.
2. Spinal cord
The spinal cord type is the most dangerous of the disease. The main lesion is cervical spine disease, which causes the spinal cord to be compressed, causing inflammation and edema. This type of patient has numbness and heaviness in the lower limbs, and it is like stepping on cotton when walking.



There will be numbness, weakness, and inflexibility of the upper limbs, and fine movements such as writing and holding chopsticks are difficult to complete. There will be paresthesias in the trunk, and there will be a belt-like binding feeling in the chest, abdomen, or lower limbs.
Some patients may also be accompanied by bladder and rectal dysfunction, such as frequent urination, urinary incontinence, and sexual dysfunction.
3. Sympathetic
The main lesion of the sympathetic type is that the lesions on the cervical spine stimulate the sympathetic nerve endings around the cervical spine.



The high incidence of this type is 30 to 45 years old, and patients often have symptoms such as dizziness, memory loss, tinnitus, hearing loss, nasal congestion, and vocal cord fatigue. Sometimes, symptoms such as foreign bodies in the pharynx and visual disturbances are also accompanied
4. Vertebral artery type
The vertebral artery type is mainly caused by the compression of the vertebral artery by the bone spur or the lack of blood supply caused by the variation of the blood vessel.



The high incidence of this type is 30 to 40 years old, and the patients will have episodic vertigo, diplopia with nystagmus, nausea and vomiting, hearing loss, and other symptoms.
These symptoms are related to changes in the position of the neck. When the head and neck are in a specific position, the patient will have lower limb weakness and cataplexy, but the consciousness is awake.
5. Esophageal type
When swallowing, patients with esophageal type experience a sense of obstruction and even progressive dysphagia.



This type is mainly caused by the huge osteophyte on the anterior edge of the cervical spine directly compressing the posterior wall of the esophagus, resulting in esophageal stenosis.
However, it may also be related to the rapid formation of bone spurs, irritating the soft tissue around the esophagus.
6. Neck
The neck type mainly occurs in the head, neck, shoulders, etc., and pain in this part will be accompanied by corresponding tenderness. In the X-ray examination, the cervical spine will have changes in curvature or instability of the intervertebral joints.
It can be seen from the above that cervical spondylosis can be divided into cervical, vertebral artery, esophageal, sympathetic, spinal, and nerve root types.


Different types have different symptoms. No matter what type it is, patients should pay attention to it and get timely treatment. The general methods of treatment of the disease include muscle relaxants, sedatives, and other drugs, as well as anterior and posterior surgeries.
Also, Read www.watchhindi.in



Hello, I am Sujeet, I am the content writer here. I write about entertainment and the latest news updates. I am a specialist in Entertainment content like movies, web series, drama series and more with experience over 5 years.







